|
^b 2
In computing, a Control key is a modifier key which, when pressed in conjunction with another key, performs a special operation (for example, ). Similarly to the Shift key, the Control key rarely performs any function when pressed by itself. The Control key is located on or near the bottom left side of most keyboards (in accordance with the international standard ISO/IEC 9995-2), with many featuring an additional one at the bottom right. On keyboards that use English abbreviations for key labeling, it is usually labeled ( or are sometimes used, but it is uncommon). Abbreviations in the language of the keyboard layout also are in use, e.g., the German keyboard layout uses () as required by the German standard DIN 2137:2012-06. There is a standardized keyboard symbol (to be used when Latin lettering is not preferred). This symbol is encoded in Unicode as U+2388 , but it is very rarely used. History On teletypewriters and computer terminals, holding down the Control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Keyboard
A computer keyboard is a built-in or peripheral input device modeled after the typewriter keyboard which uses an arrangement of buttons or Push-button, keys to act as Mechanical keyboard, mechanical levers or Electronic switching system, electronic switches. Replacing early punched cards and paper tape technology, interaction via teleprinter-style keyboards have been the main input device, input method for computers since the 1970s, supplemented by the computer mouse since the 1980s, and the touchscreen since the 2000s. Keyboard keys (buttons) typically have a set of characters Engraving, engraved or Printing, printed on them, and each press of a key typically corresponds to a single written symbol. However, producing some symbols may require pressing and holding several keys simultaneously or in sequence. While most keys produce character (computing), characters (Letter (alphabet), letters, Numerical digit, numbers or symbols), other keys (such as the escape key) can prompt the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
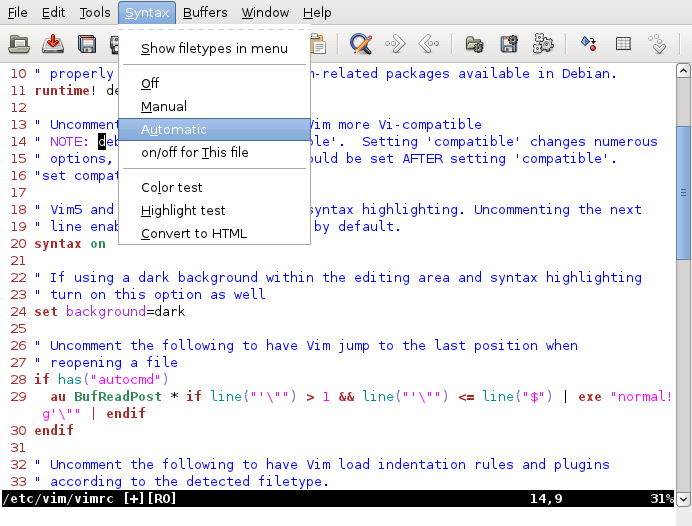
Vim (text Editor)
Vim (; : "Vim is pronounced as one word, like Jim, not vi-ai-em. It's written with a capital, since it's a name, again like Jim." ''vi improved'') is a free and open-source, screen-based text editor program. It is an improved Clone (computing), clone of Bill Joy's vi (text editor), vi. Vim's author, Bram Moolenaar, derived Vim from a port of the Stevie (text editor), Stevie editor for Amiga and released a version to the public in 1991. Vim is designed for use both from a command-line interface and as a standalone application in a graphical user interface. Since its release for the Amiga, cross-platform development has made it available on #Availability, many other systems. In 2018, it was voted the most popular editor amongst ''Linux Journal'' readers; in 2015 the Stack Overflow developer survey found it to be the third most popular text edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caret Notation
Caret notation is a notation for control characters in ASCII. The notation assigns to control-code 1, sequentially through the alphabet to assigned to control-code 26 (0x1A). For the control-codes outside of the range 1–26, the notation extends to the adjacent, non-alphabetic ASCII characters. Often a control character can be typed on a keyboard by holding down the and typing the character shown after the caret. The notation is often used to describe keyboard shortcuts even though the control character is not actually used (as in "type ^X to Cut, copy, and paste, cut the text"). The meaning or interpretation of, or response to the individual control-codes is ''not'' prescribed by the caret notation. Description The notation consists of a ''caret (computing), caret'' () followed by a single character (usually a capital letter). The character has the ASCII code equal to the control code with the bit representing 0x40 reversed. A useful mnemonic, this has the eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Happy Hacking Keyboard
The Happy Hacking Keyboard (HHKB) is a small computer keyboard produced by PFU Limited of Japan, codeveloped with Japanese computer scientist and pioneer Eiiti Wada. Its reduction of keys from the common 104-key layout down to 60 keys in the professional series is the basis for it having smaller overall proportions, yet full-sized keys. It returns the control key to its original position as on the early 84-key IBM Personal Computer/AT and IBM Personal Computer XT, XT layouts. The current models in production are the Happy Hacking Keyboard Professional Classic, Professional Hybrid (wired/wireless dual connectivity), and Professional Hybrid Type-S (silenced variant of Hybrid) all in either dark or light colorschemes, and either blank or printed keycaps. Professional Hybrid models are also available in Japanese input method, Japanese layout. History Beginnings Frustrated that each new computer system came with a new keyboard layout that became increasingly complex, Wada sought t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, Reduced instruction set computer, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualization, virtualized computing. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California (part of Silicon Valley), on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center. Sun products included computer servers and workstations built on its own Reduced instruction set computer, RISC-based SPARC processor architecture, as well as on x86-based AMD Opteron and Intel Xeon processors. Sun also developed its own computer storage, storage systems and a suite of software products, including the Unix-based SunOS and later Solaris operating system, Solaris operating s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems ( SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE ( HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). The early versions of Unix—which are retrospectively referred to as " Research Unix"—ran on computers such as the PDP-11 and VAX; Unix was commonly used on minicomputers and mainframes from the 1970s onwards. It distinguished itself from its predecessors as the first portable operating system: almost the entire operating system is written in the C programming language (in 1973), which allows U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the List of IBM Personal Computer models, IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible ''de facto'' standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team of engineers and designers at IBM, International Business Machines (IBM), directed by William C. Lowe and Philip Don Estridge in Boca Raton, Florida. Powered by an x86-architecture Intel 8088 processor, the machine was based on open architecture and third-party peripherals. Over time, expansion cards and software technology increased to support it. The PC had influence of the IBM PC on the personal computer market, a substantial influence on the personal computer market; the specifications of the IBM PC became one of the most popular computer design standards in the world. The only significant competition it faced from a non-compatible platform throughout the 1980s was from Apple Inc., Apple's Maci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADM-3A
The ADM-3A is an early influential video display terminal, introduced in 1976. It was manufactured by Lear Siegler and has a 12-inch screen displaying 12 or 24 lines of 80 characters. It set a new industry low single unit price of $995. Its "dumb terminal" nickname came from some of the original trade publication advertisements. It quickly became commercially successful because of the rapid increase of computer communications speeds, and because of new minicomputer and microcomputer systems released to the market which required inexpensive operator consoles. History Lear Siegler, Inc. (LSI) manufactured its first video display terminal in 1972 – the 7700A. In 1973, LSI hired a new head of engineering, Jim Placak. He and his team created the ADM-1 later that year. It set a new pricing low in the industry at $1,500. Its lower cost was primarily due to a unique single printed circuit board design. In early 1973 the LSI division in Anaheim, California that manufactured th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lear-Siegler
Lear Siegler Incorporated (LSI) is a diverse American corporation established in 1962. Its products range from car seats and brakes to weapons control systems for military fighter planes. The company's more than $2 billion-a-year annual sales comes from three major areas: aerospace-technology, automotive parts, and industrial-commercial. The company, however, is basically anonymous, since its products are either unmarked or bear only the label "LSI". Lear Siegler went private in 1987. LSI is sometimes confused with Learjet, which manufactures executive jets. History Siegler The Siegler Corporation was incorporated in December 1950 as the Siegler Heating Company. Originally a maker of climate control equipment, the company changed its name to Siegler Corporation after merging with Siegler Enamel Range Company Inc. in 1954. In that year, John G. Brooks, a flamboyant entrepreneur, and nine other associates bought the Siegler Corporation of Centralia, Illinois, for $3.3 million; $3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |